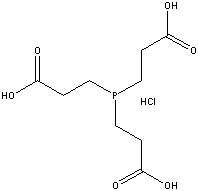
TCEP HCl(Protein Modifier) M115 Tris( 2-carboxyethyl )phosphine hydrochloride[ 51805-45-9 ] f.w.: 286.6 daltons |
TCEP HCl is a potent versatile odorless thiol-free reducing agent with many applications in protein chemistry and proteomic research centered in the quantitative ease of reducing disulfide bonds. The versatile compound is readily soluble and very stable in aqueous solutions. In fact TCEP HCl is stable in aqueous, acidic and basic solutions. TCEP HCl reduces disulfide bonds as effectively as dithiothreitol ( DTT ), but unlike dithiothreitol ( DTT ) and other thiol reducing agents, it does not need to be removed prior to certain sulfhydryl reactive cross linking reactions. These are but a few of the reasons TCEP HCl is a superior reagent than dithiothreitol ( DTT ) for use in reducing disulfide bonds in protein chemistry and proteomic research.
| Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|
| 1gm | $43.00 |  |
| 2gm + | $59.00 |  |
| 5gm + | $102.00 |  |
| 10gm + | $133.00 |  |
| 25gm + | $322.00 |  |
| 100gm + | $1134.00 |  |
| Download***Certificate of Analysis*** | ||
| Download***Monograph*** | ||
| Download***MSDS*** | ||
Product is a superior alternative to DTT. The product is odorless, non-volatile and stable in air. Dilute solutions in air show no appreciable oxidation. Reduces organic disulfides to thiols rapidly and quantitatively in water. The reaction is reversible. Does not react with other functional groups on proteins.
- K. C., Dixon, J.E., Anal. Biochem, 161, 524-528 (1987).
- Schonberg, A., Chem Ber., 163-164 (1935).
- Rauhut, M., et. al., JACS, 81, 1103-1107 (1959).
- Chen, C.S., Fujimoto, Y, girdoukas, G., Sih, C.J., JACS, 109, 6825-6309 (1987).
- Kirley, T.L., Anal. Biochem, 180, 231-236 (1989).
- Andrews, P C., Dixon, J.E., Anal. Biochem., 161, 524-528 (1987).
- Y., Girdoukas, G.Sih, C.J., JACS, 109, 6825-6309 (1987).
- Houk, J., Whitesides, G.M., JACS, 109, 6825-6836 (1987).
- Grayson, M., Farley, C.E., Chimie Organique du l du Centre Natl de la Recherche Scientifique, No. 182 CNRS, Paris, 275-284 (1970).
- Overman, L.E OConner, E.M., JACS, 98, 771-775 (1977).
- Rosenfield, R.E., Parthasarthy, R., Dunitis, J.D., JACS, 99, 4860-4862 (1977).
- Ruegg, U.T. and Rudinger, J., Methods Enzymology, 47, 111-126, (1977).
- Burns, J.A., et al, J. Org. Chem, 56, 2648-2650, (1991).
- Mery, J., et al,, Peptide Protein Research, 42, 44-52, (1993).
- Gray, W. R., Protein Science, 2, 1732-1748, (1993).
- Fisher, W.H., et al, Mass Spectrometry, 7, 225-228, (1993).
- Bieri, S, et al, Biochemistry, 34, 13059-13065, (1995).
- Tam, J., P,, et al, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 12485-12489, (1995).
- Blauenstein, P., et al, Eur. J. Nucl. Med., 22, 690-698 (1995).
- Gorman, J.J., et al, Rapid Communications Mass Spectrometry, 10, 529-536 (1996).
- Kiirsch, T., et al, Protein Expression Purification, 8, 75-84 (1996).
- Wu, J. and Watson, J.T., Protein Science, 6, 391-398 (1997).
- Bernard, C. L., et al, Exp. Brain Res., 113, 343-352 (1997).
- Huh, K. and Wenthold, R.J., Journal Biological Chemistry, 274, 151-151 (1999).
- Oda, Y. et al, Nature Biotech, 19, 379-382 (2001).
- Odorless and non-volatile
- Solid is stable in air for several months
- Dilute TCEP solutions in air show no appreciable oxidation up to at least 72 hours pH<7.66
- Solubility in water 310gm/liter
- TCEP reduces organic disulfides to thiols rapidly and quantitatively in water
- More complete reductions than 1,4-dithiothreitol ( DTT ), Clelands reagent
- Even very stable alkyl disulfides are completely reduced at room temperature and pH 5 in less than 5 min.
- Dilute (1mM) TCEP solutions react rapidly at room temperature
- The strength of the phosphorus-oxygen bond makes the reaction irreversible
- Kinetics rather than thermodynamics controls the reduction
- Selectivity!
- TCEP is selective for disulfides
- TCEP does not react with other functional groups on proteins
- Unreactive towards many common alkylating reagents so reductions have been carried out simultaneously with alkylations


